The Path to Healthy Eating: Cultivating a Balanced and Nutritious Lifestyle
Healthy eating is more than just a dietary choice; it is a lifestyle that fosters long-term well-being. It involves consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods that nourish the body, maintain energy levels, and support optimal health. This comprehensive approach to nutrition goes beyond counting calories or adhering to restrictive diets. Instead, it embraces the principles of balance, moderation, and diversity in food choices. Here’s how to embark on a journey toward healthy eating and the benefits it brings.
1. The Principles of Balanced Nutrition
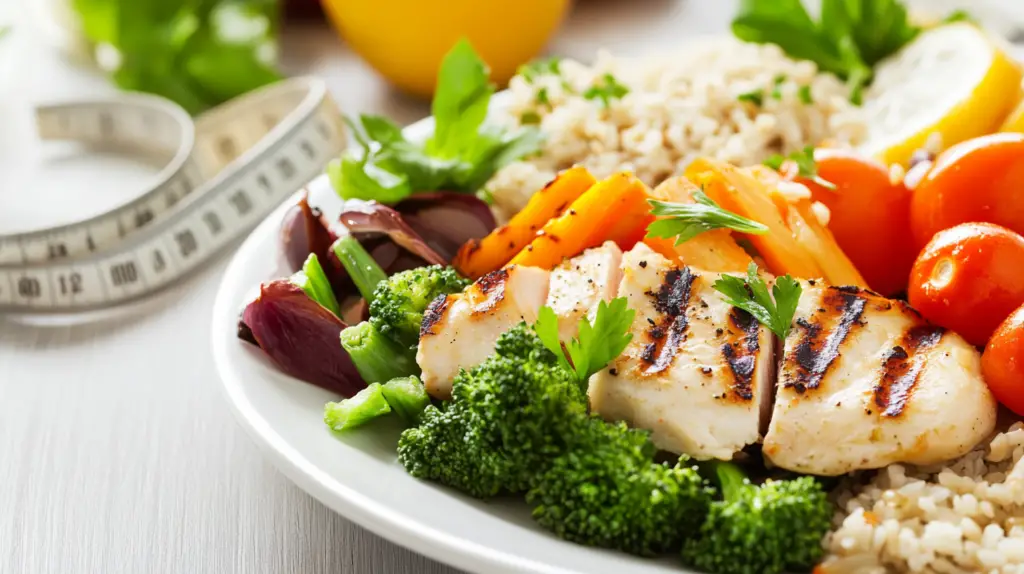
At the core of healthy eating is the concept of balance. A balanced diet includes a diverse range of foods from all major food groups: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and healthy fats. Each food group provides essential nutrients that perform distinct functions in the body. For example, carbohydrates are the primary energy source, while proteins are crucial for tissue repair and muscle maintenance. Healthy fats support brain function and hormone production, and a variety of vitamins and minerals facilitate countless biochemical processes.
Incorporating foods from each group in appropriate proportions ensures that the body receives all the necessary nutrients. The key is to focus on whole and minimally processed foods, as these retain more nutrients than their heavily processed counterparts. Choosing whole grains like quinoa and oats over refined grains, for instance, provides more fiber, which is beneficial for digestion and blood sugar control.
Hydration also plays an integral role in balanced nutrition. Water is essential for metabolic processes, detoxification, and maintaining body temperature. Drinking an adequate amount of water daily supports cellular functions and helps prevent fatigue and dehydration.
2. The Impact of Healthy Eating on Physical Health
Embracing healthy eating habits has a profound effect on physical health. A nutrient-rich diet helps to prevent chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and certain types of cancer. The antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables, for instance, combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation, which are linked to numerous chronic illnesses.
Maintaining a diet that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, nuts, and seeds, supports cardiovascular health by lowering cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease. Meanwhile, the inclusion of lean proteins and plant-based protein sources helps build and repair muscle tissue, especially important for those who engage in regular physical activity.
In addition to physical benefits, a healthy diet can enhance the immune system. Nutrients such as vitamin C, zinc, and selenium, commonly found in citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds, strengthen the body’s defense mechanisms against infections and diseases. The gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in immune function, thrives on a diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics, found in foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and legumes.
3. The Psychological Benefits of a Nutrient-Dense Diet
Healthy eating not only impacts physical health but also significantly affects mental well-being. There is a growing body of evidence linking nutrition to mood and cognitive function. Diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants have been shown to improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression. These nutrients aid in neurotransmitter synthesis and protect brain cells from damage, thereby enhancing overall mental clarity and emotional stability.
Conversely, diets high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can contribute to feelings of lethargy, irritability, and even anxiety. Sugar spikes and crashes, common with high-sugar diets, can cause mood swings and affect energy levels. Transitioning to a diet that emphasizes whole foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels, leading to more consistent energy and mood.
Mindful eating, which involves paying attention to the sensations and experiences associated with food, further promotes psychological well-being. This practice encourages a positive relationship with food, reduces overeating, and fosters gratitude for nourishing the body.
4. Practical Tips for Incorporating Healthy Eating into Daily Life
Adopting healthy eating habits does not have to be overwhelming. Small, incremental changes can make a significant difference over time. Start by gradually increasing the intake of fruits and vegetables, aiming for at least five servings per day. Experimenting with different cooking methods, such as roasting, steaming, or grilling, can enhance the natural flavors of produce while retaining nutrients.
Meal planning and preparation are practical strategies to maintain a balanced diet. By setting aside time each week to plan meals and snacks, it becomes easier to make nutritious choices and avoid impulsive eating. Preparing meals at home also allows for greater control over ingredients, portion sizes, and cooking methods.
Reading food labels is another useful habit for informed eating. Look for products with fewer ingredients and minimal added sugars or unhealthy fats. Understanding portion sizes and caloric needs can further aid in making healthy food choices without feeling deprived.
Lastly, it is important to allow for flexibility and occasional indulgences. Healthy eating is not about strict dietary restrictions but about cultivating a sustainable approach that supports overall well-being. Enjoying a treat now and then, in moderation, can be part of a balanced diet.
5. The Future of Healthy Eating: Trends and Innovations
The landscape of healthy eating continues to evolve, with emerging trends and innovations that aim to make nutritious food more accessible and appealing. One significant trend is the rise of plant-based diets, which are gaining popularity for their health benefits and lower environmental impact. Plant-based proteins, such as lentils, chickpeas, and tofu, are being incorporated into mainstream diets as more people seek alternatives to animal products.
Another growing movement is the focus on personalized nutrition, where dietary recommendations are tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health status. Advances in nutrigenomics, which studies the relationship between nutrition and genes, are paving the way for customized dietary plans that optimize health based on personal biological factors.
Technology is also transforming the way people approach healthy eating. The advent of smart kitchen appliances, such as air fryers and sous-vide cookers, encourages home cooking by simplifying meal preparation while preserving nutritional quality. Additionally, food tracking apps and wearable devices help individuals monitor their dietary habits and make informed adjustments to support their health goals.
The future of healthy eating is promising, with continued innovation driving a more personalized, convenient, and sustainable approach to nutrition. By embracing these advancements while adhering to the timeless principles of balanced eating, individuals can cultivate a lifestyle that supports both current health and future vitality.